Cutting and Penetrating Instrument Injuries and First Aid at Work
1. Injuries to Cutting and Piercing Tools: An Overview
Cutting and piercing tools in workplaces are among the equipment frequently used, especially in the manufacturing, construction, agriculture, health and food sectors. Dec. Injuries that occur during the use of such tools are among the serious accidents that threaten the health of employees. Dec. Cutting and piercing tools can be various objects such as knives, utility knives, screwdrivers, pieces of glass, metal edges and syringe needles.
Such injuries usually occur due to distraction at work, lack of proper protective equipment, or improper use of tools. Injuries can be a wide range, from superficial cuts to deep wounds, tendon or November muscle damage, blood loss and risk of infection.
2. Prevention of Cutting and Penetrating Instrument Injuries
It is important to take the following measures to prevent such accidents in the workplace:
Education and Awareness Raising: Employees should receive regular training on the safe use of cutting and piercing tools.
Use of Protective Equipment: Protective equipment such as gloves, glasses should be used and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be provided to each employee.
Maintenance of Tools: Regular maintenance of cutting tools should be carried out, rusted or damaged tools should not be used.
Safe Working Area: The working environment should be kept tidy and clean, cutting and drilling tools should be stored safely.Jul.
Marking and Warnings: Necessary warning signs and markings should be made in risky areas.
3. First Aid for Cutting and Penetrating Instrument Injuries
Quick and accurate first aid intervention for cutting and penetrating instrument injuries can reduce the size of the injury and prevent more serious consequences. Depending on the type of injury, first aid can be performed as follows:
A. Superficial Cuts:
Cleaning the Wound: If the injury is superficial, the wound area is cleaned of dirt and foreign substances by washing with clean water.Jul.
Stopping Bleeding: It is tried to stop bleeding by applying light pressure with the help of a clean cloth or bandage. Jul.
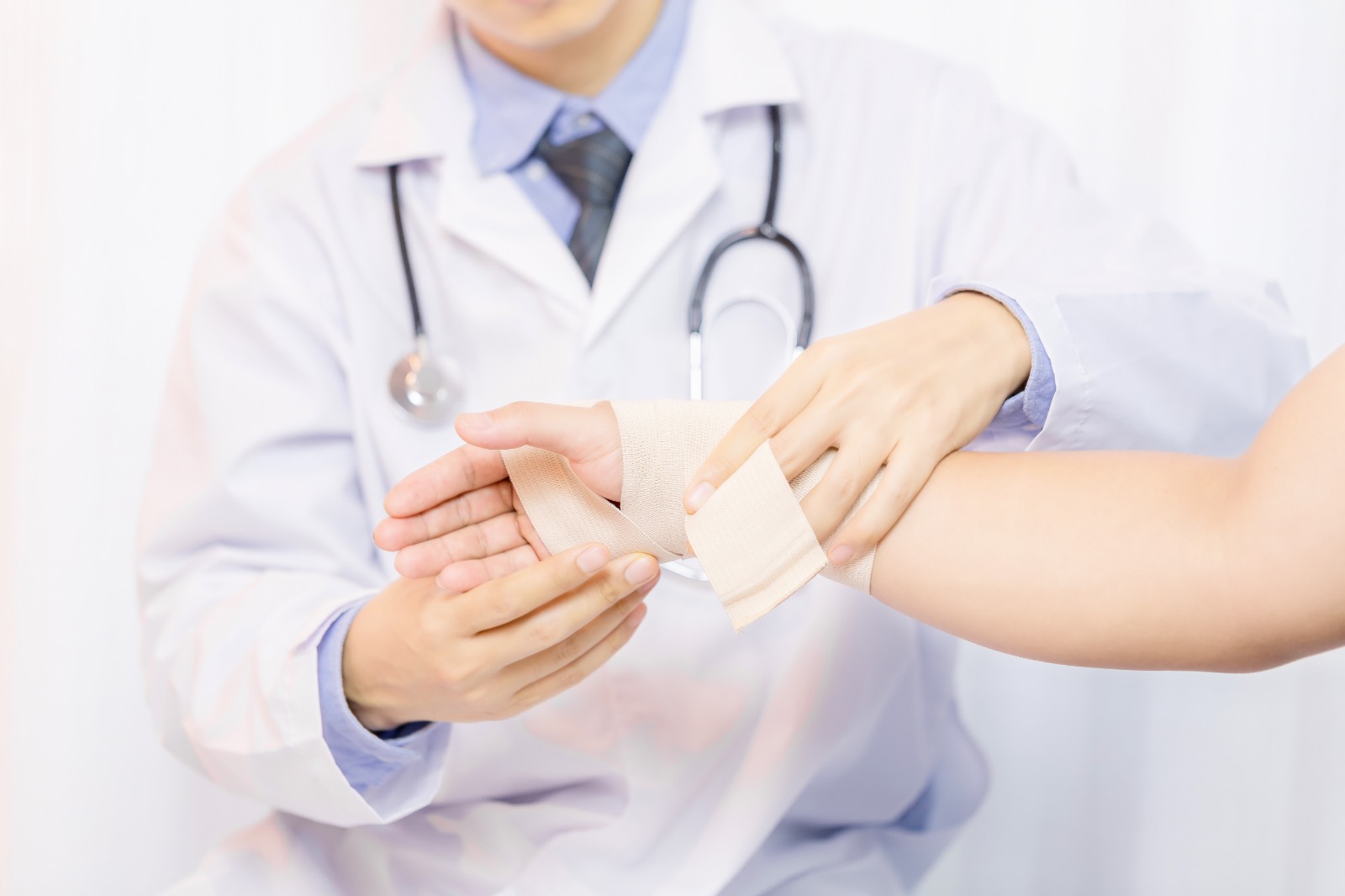
Closing the Wound: After the bleeding stops, the wound area is closed with a sterile bandage and the wound is kept under control.
Use of Antiseptic: An antiseptic solution can be used to reduce the risk of infection.
B. Deep Cuts and Severe Bleeding:
Bleeding Control: If the injury is deep and the bleeding is intense, pressure is applied to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage. Jul. Pressure will help reduce bleeding.
Keeping the Injured Area High: If possible, the injured area can be slowed down by lifting the blood flow above the heart level.
Wound Dressing: After the wound is cleaned, it is wrapped with a sterile cloth. If the bleeding continues, a tampon is performed by increasing the pressure.
Call for Professional Help: In case of deep cuts, 112 Emergency Services should be called without wasting time and medical assistance should be requested. Bleeding control should be maintained during the patient's transplant.
C. Penetrating Injuries (Needle, Screwdriver, Piece of Glass, etc.):
Not Touching the Wound: If the penetrating object is inside the wound, it is important not to try to remove the object, because this can increase bleeding and lead to further tissue damage.
Protection Around the Wound: The wound is supported around with a sterile cloth without contact.
Bleeding Control: An attempt is made to control the bleeding before the piercing object is removed. Care should be taken when applying pressure to the injured area.
Medical Assistance: Emergency medical assistance should be called and the penetrating object should be removed by specialized medical personnel.
D. Risk of Infection and Tetanus:
Infection Control: The risk of infection is quite high in injuries to cutting and piercing tools. For this reason, the wound should be cleaned with sterile materials if possible after the injury. Antiseptic solutions can also be used to reduce the risk of infection.
Tetanus Vaccine: The injured person should check whether he has received a tetanus vaccine. If there is no tetanus vaccine or if it has been 10 years, tetanus vaccine should be given in medical units.
4. Responsibilities of the Employer in Cutting and Penetrating Instrument Injuries
Employers have various legal and occupational health and safety obligations against cutting and piercing instrument injuries:
Risk Analysis and Evaluation: A risk assessment should be made regarding the use of cutting and piercing tools in the workplace. Hazardous areas and jobs should be identified, and the protection of employees in these areas should be ensured.
Training: The employer should regularly provide training to employees on safe use of tools and first aid.
Provision of Protective Equipment: All personnel working with cutting and piercing tools at the workplace should be provided with appropriate personal protective equipment and the use of these equipment should be encouraged.
First Aid Equipment: First aid materials (sterile cloths, bandages, antiseptics, etc.) that can be intervened at any time in the workplace.) should be kept and employees should be made aware of first aid.
Injuries from cutting and piercing tools at work are accidents that can have serious consequences. In order to prevent such injuries, the rigorous implementation of occupational safety measures, the use of protective equipment and education are of great importance. In addition, a quick and accurate first aid intervention in the event of accidents can minimize the impact of injuries and prevent more serious health problems. The fact that employers educate their employees on this issue and take the necessary safety measures will significantly reduce occupational accidents.
Üniversal OSGB
Occupational Safety and Worker Health Center


